Overview of Artificial Intelligence
Part 1
CS123, Intro to AI
| Topics | |
|---|---|
| Overview of AI | Generative AI |
| History and application of AI | Prompt engineering |
| Machine Learning | Custom chatbot creation |
| Neural networks and deep learning | Social and ethical issues of AI |
Table of Contents
What is AI?What is intelligence?Your Turn: How would you define intelligence?Types of AISymbolic AI vs. ANNsSymbolic AIArtificial Neural NetworksGenerative AI Narrow AIExamples of Narrow AIYour Turn: Can you think of other examples of narrow AI?General AIIs chatGPT a General AI System?Reference
What is AI?
AI, or Artificial Intelligence, is a field of computer science that aims to create computer systems capable of doing things that would normally require human intelligence. These things include: thinking, reasoning, learning, using natural language, problem solving, and decision making1.
We need to know the definitions of words so that we can understand each other. Here is the dictionary definition of Intelligence:
What is intelligence?
The ability to learn or understand or to deal with new or trying situations. Also : the skilled use of reason.
The ability to apply knowledge to manipulate one's environment or to think abstractly as measured by objective criteria (such as tests)
—Merriam-Webster Dictionary
Your Turn: How would you define intelligence?
Is your definition different from the dictionary definition?
Later we will discus whether or not current AI systems are really intelligent.
Types of AI
There are two major types of AI: symbolic AI and artificial neural networks (ANN). There are also hybrid systems that use both symbolic AI and ANNs.
AI can also be categorized into two categories: narrow AI and general AI.
Symbolic AI vs. ANNs
Symbolic AI
Also known as classical or Good Old Fashioned AI (GOFAI).
It focuses on processing and manipulating symbols or concepts, rather than numerical data.
Uses logic-based programming, where rules and algorithms are used to make decisions.
The decision-making is transparent. The reasoning process can be traced back to the logical rules that were applied.
Simplified example from the medical field, diagnosing a patient's symptoms:
IF patient has a fever AND patient has a cough AND patient has difficulty breathing THEN patient may have pneumonia.In "Essentials of AI", you will see an example application of AI for playing tic-tac-toe in which a decision tree is built and an algorithm is used to follow branches of the tree to find moves that will lead to winning the game.
We'll work through a similar example together in the next class.
Artificial Neural Networks
Also known as connectionism.
A computer model inspired by the structure and function of neural networks in the brain. It uses a network of connections to map data input data to a desired output.
Neural networks are built using machine learning, in which they are trained an large amounts of data that contains examples of the things the neural network should recognize and process
They are not transparent. It is very difficult (if not impossible) to determine which set of connections were followed to reach a given decision.
Example, image recognition:
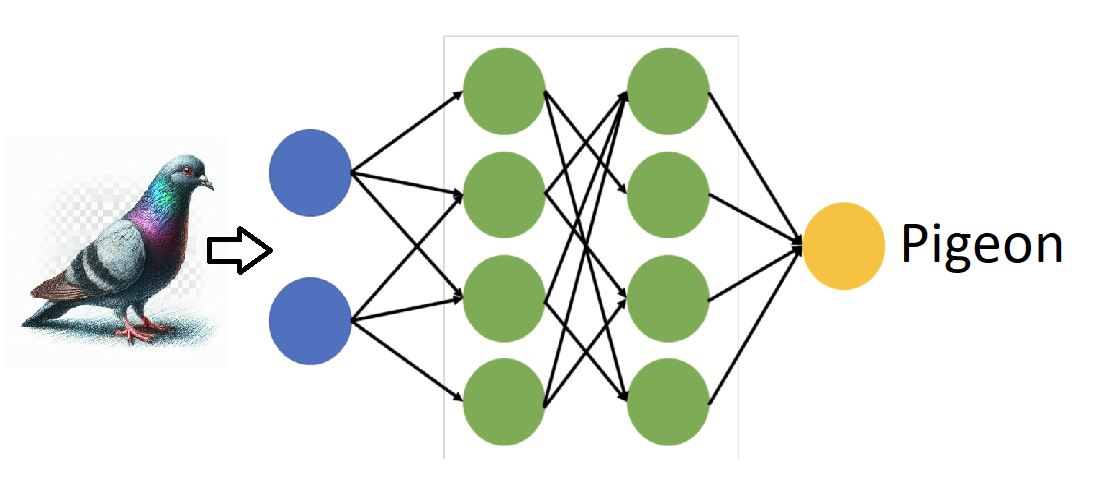
Generative AI
Can create "original" content such as text, images, video, audio, or software code in response to a user's prompt.
Uses Deep learning models (LLMs), which work by identifying and encoding the patterns and relationships in huge amounts of data encoded into an ANN.
Unlike GOFAI, which makes predictions based on data by applying rules, generative AI is trained to create new data using a sophisticated ANN, which means that the process by which it operates is not transparent.
GPT Chatbots
A Generative Pretrained Transformer (GPT) chatbot produces a string of output words, based on a prompt by using probability to predict the next most likely word:
Input: The chatbot receives a user’s prompt or instruction.
Tokenization: The AI model breaks apart the input into more manageable tokens (words or parts of words).
Probability Calculation: The model calculates the probability of each possible next word (or token) based on the data set it was trained on.
Word Selection: The model selects the next word with the highest probability, but with some randomness thrown in to simulate creativity.
Response Generation: This process is repeated until a complete response is generated.
Output: The generated response is returned to the user.
Narrow AI
These are systems designed to perform a specific task and can only operate under a limited set of constraints.
Examples of Narrow AI
Digital Voice Assistants: Siri, Alexa, and Google Assistant are examples of Narrow AI. They understand and respond to voice commands and can perform specific tasks like setting alarms, making phone calls, and answering questions.
Recommendation Systems: The recommendation algorithms used by platforms like Netflix, Amazon, and Spotify are examples of Narrow AI. They analyze your past behavior and preferences to suggest content you might like.
Email Filtering: Email services use Narrow AI to filter out spam and categorize emails into different folders.
Weather Forecasting: Narrow AI is used in predicting weather conditions based on a vast amount of meteorological data.
Image Recognition Systems: These are used in self-driving cars to recognize traffic signs, pedestrians, and other vehicles.
Your Turn: Can you think of other examples of narrow AI?
General AI
Also known as AGI (Artificial General Intelligence) are systems that possess the ability to perform any intellectual task that a human being can do. They can understand, learn, adapt, and implement knowledge in different domains. This type of AI is purely theoretical at this point with no practical examples in use today.
Is chatGPT a General AI System?
ChatGPT is not an example of General AI. It's actually Narrow AI. While it's quite advanced and can generate human-like text based on prompts, it's still designed for a specific task: text generation. It doesn't have an understanding of the world in the way humans do, and it can't apply knowledge from one domain to another in the way a human would. It operates based on patterns in the data it was trained on and doesn't have understanding[^3] of the text it generates.
Reference
Artificial Intelligence, A Modern Approach—2010, 3rd Ed. Pearson
Elements of AI—The University of Helsinki and MinnaLearn, 2024
Understanding the Different Types of Artificial Intelligence—IBM
 Intro to AI Lecture Notes by Brian Bird, written in , are licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
Intro to AI Lecture Notes by Brian Bird, written in , are licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.